Dental Topics
Dental Radiographs (X-Rays)
X-rays allow dentists to diagnose and treat conditions that cannot be detected during a clinical examination. For example, X-rays are helpful to “see” cavities between teeth, diagnose bone diseases, evaluate the results of an injury, and plan orthodontic treatment.
Dental care is more comfortable for your child when problems are found and treated early.
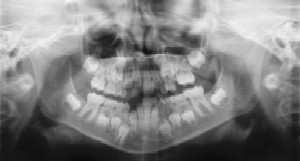
In general, children need X-rays more often than adults because their mouths grow and change rapidly. The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry recommends radiographs and examinations every six months for children with a high risk of tooth decay.
Fluoride Varnish
Fluoride varnish is a painless dental treatment that can help prevent, slow down, or stop tooth decay (cavities) from getting worse. Fluoride is a mineral that works by strengthening tooth enamel (outer coating of teeth).
Keep in mind that fluoride varnish cannot completely prevent cavities. Fluoride varnish is most effective when a child is also brushing, using the right amount of toothpaste with fluoride, flossing regularly, getting regular dental care, and eating a healthy diet.
Dental Sealants
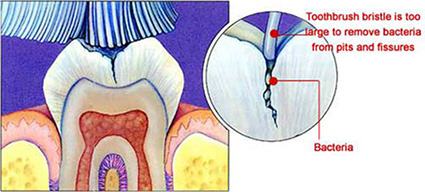
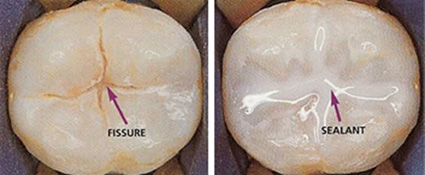
Sealants are white, plastic, protective coatings that are placed on the tops or chewing surfaces of back teeth (molars) to help prevent cavities. Molars contain deep groves that are often times hard to keep clean. The sealant material fills the groves and protects them from the bacteria that can cause cavities.
Fillings
Silver and white colored filling materials may be used to restore (fix) teeth with small to moderate sized cavities.
The material selection is determined by the following:
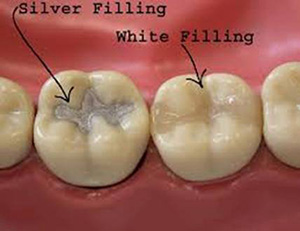
- The location and size of the cavity
- The child’s risk and rate of dental decay
- The child’s ability to cooperate for treatment
Pediatric Crowns
The crowns used to restore and protect primary (baby) teeth are pre-formed, placed in one visit, and are made of stainless steel.
These crowns are silver in color and last a long time. With proper home care, these restorations will act as natural teeth and will fall out normally with the baby tooth.
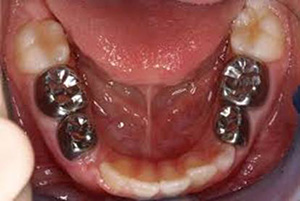
When are Stainless Steel Crowns used?
- When teeth have large cavities or are fractured
- When children have a high risk and/or rate of dental decay
- Following nerve treatment in primary (baby) teeth
Stainless Steel Crowns with white coatings may be used for restoring front teeth.
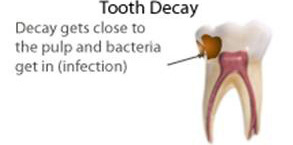
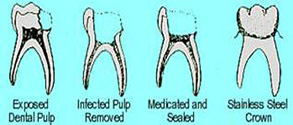
Pulp Treatment (Pulpotomy)
Some cavities are so deep that they extend to the nerve of the tooth, often (but not always) causing pain and discomfort. When this happens, the infected part of the nerve must be removed. The remaining healthy nerve will be left intact and medicated. The purpose of a Pulpotomy is to prevent the need for an extraction. Stainless Steel Crowns are then placed to ensure proper chewing and to maintain space for permanent teeth.
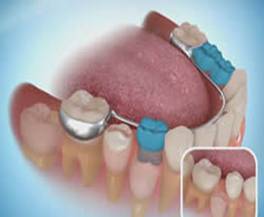
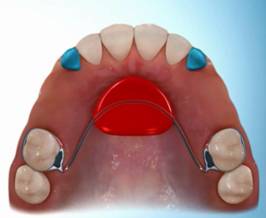
Space Maintainers
Primary teeth may have to be removed (extracted) for the following reasons:
- Severe decay
- Infection (abscess)
- Crowding or other orthodontic issues
Space Maintainers may be used when a primary (baby) tooth has been prematurely lost to temporarily hold space for the permanent tooth. In some cases, teeth on either side of the extraction site can drift and prevent the permanent tooth from erupting (coming in) into its proper position.